Toru Nakagawa (Osaka Gakuin Univ.),
Mar. - Oct., 2000
Appendix A. "Solution to the problems" (Errata by Souchkov, Mar. 2000)
General comments:
All Substance-Field formulas were redrawn in Winword format.
All numeric entries referring to
fields and substances in SFMs were marked in the text of problems.
| c. 211 | Place the formula which appeared in the answer to THE STORY OF A HAPLESS GAS-EXPANSION MACHINE below the answer to Flaunting Flag Wanted. (see revised edition) | |
| c.211 |
 |
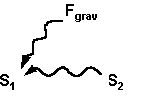 |
| c.214 | Insert:Problem 39 ? No target answer. | |
| c.215 |  |
 |
| 216 | Move "Both variants should be considered" below the formula | |
| 216 | If thermal field is to be directly transformed into a signal field, one should use physical effects such as thermomechanical effect (bimetal, nitinol), thermoelectric effects (generation of a thermo-emf). | If thermal field is to be directly transformed into a signal field, one should use physical effects such as thermomechanical effect (bimetal, nitinol), thermoelectric effects (generation of a thermo-emf), thermomagnetic effects (transition through the Curie point). |
| 216 | Among others, geometrical effects can be employed here too: at the critical depth.... | Among others, thermo-chemical effects can be employed here too: at the critical depth.... |
| c.217 | Problem 80. Soviet Patent no. 845 872 | Problem 80. Soviet Patent no. 845 871 |
| 217 | Move the figure with balls after the answer to the problem | |
| c.218 | 2). the method of strong currents: thousands of amperes can stop a crack in fragment of a second. | 2). the method of strong currents: thousands of amperes can stop a crack in a microsecond. |
Appendix A. (Errata
by Nakagawa, July 2000)
| P L E/Q | is | has to be [or questions, suggestions, etc.] |
| 211 t12 E | THE STORY OF A HAPLESS GAS-EXPANSION MACHINE. | [This line should be moved below the first figure.] |
| 212 t15 E | Problem 24. Instead of water, it is necessary to use a magnetic liquid with changes it density | Problem 24. Instead of water, it is necessary to use a magnetic liquid which changes it density |
| 212 t30 Q | The liquid solution can be put under subject to | The electrolytic solution can be put under subject to |
| 215 t11 E | There is a way out. The characters drink water and pretend they are dying. | There shouldbe a way out. The characters drink water and pretend they are dead. |
| 216 t1 S | when external layers are cooled, and the internal layers that prevent them from shrinking. | when external layers are cooled, the internal layers prevent them from shrinking. |
| 216 t20-21 S | thermoelectric effects (generation of a thermo-emf) | thermoelectric effects (generation of a thermo-electromotive force) |
| 216 b13 E | is be made of nitinol | is made of nitinol |
| 217 t2 Q | corund balls of 40-50 mcm diameter | corundum balls of 40-50 ?m diameter |
| 217 t3 S | They disperse the beam without being heated. | They scatter the beam without being heated. |
| 217 t10 Q | that can tint flame, a phosphorescent substance, | that can tint flame, a fluorescent substance, |
| 217 First Fig. E | [At the right of the first figure, a black vertical bar is shown.] | [Delete the black vertical bar.] |
| 218 t3 E | delivered to the bucket, waterwill move | delivered to the bucket, water will move |
| 218 t6 S | exhaust fumes go from the silencer into the body of the dump truck | exhaust fumes go from the silencer into the load of the dump truck |
| 218 b15 Q | developed in Federative Republic of Germany | developed in Federal Republic of Germany |
| 218 b9 S | is laid on one side. If thawing occurs, | is laid on one side. And then it is put upright. If thawing occurs, |
| 218 b8 E | The width of the horizontal layer indicates | The depth of the horizontal layer indicates |
| 218 b4 S | Oxygen disappears from the sucker, leaving vacuum inside | Oxygen disappears from the sucker, reducing the pressure inside |
| 219 t20 S | Problem 109. Electric current is transferred through the thread. | Problem 109. Electric current is transferred through the wire. |
| 219 b4 E | Analysis of drop index and mean drop dimensions). | Analysis of drop index and mean drop dimensions. |
Appendix A. (Questions/Comments
by Nakagawa and Answers by Souchkov)
| P L E/Q/C/S | Is | Has to be [or Question] | Answer |
| 211 t1 S | SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS. | A.
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS.
[Sections in appendices are numbered as A, B, ...' |
ok |
| 211 t13 E | [The top
figure is placed below the line of
"THE STORY OF ...".] |
[The top
figure is placed above the line of
"THE STORY OF ...".] |
ok |
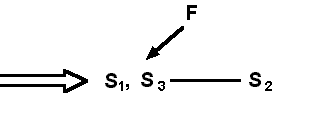
| 211 b11 E | the wind (F2) blows them away | the wind (S2) blows them away | yes |
| 211 b7 S | F [in the bottom figure] | Fgrav | yes |
| 212 t9 S | F [in the top figure] | Fgrav | |
| 212 t15-16 E | it is necessary to use a magnetic liquid with changes its density under magnetic field and does not pour out of the chute at any angle. | it is
necessary to use a magnetic liquid which changes
its apparent density under magnetic field and does not pour out of the
chute at any angle.
[or rather: it is necessary to use a magnetic liquid which does not pour out of the chute at any angle under magnetic field. ] |
yes |
| 212 b13 Q/S | The liquid solution can be put under subject to electric current | The electrolytic solution can be put under subject to electric current | yes |
| 213 t7 Q | Problem 30. Peppers can be peeled by air. | [What kind of peppers do you mean? Are they plants of black peppers or green peppers? Which part of the peppers do you want to have later?] | This type
of pepper is known in Latin as Capsicum.
It consists of a thick shell (red or green) which is used for the meals and seeds located inside the shell that have to be removed. The problem is how to remove the seeds. |
|
214 b9 C |
Problem 43. No target solution. | [I am
going to attach the following footnote:]
Footnote: See "Staircases Design of High Buildings Prepared against Fire - TRIZ/USIT Case Study" by Toru Nakagawa, in "TRIZ Home Page in Japan", Aug. 2000, URL: http://www.osaka-gu.ac.jp/php/nakagawa/TRIZ/. |
ok |
| 215 t12 S | There is a way out. The characters drink water and pretend they are dying. | There should be a way out. The characters drink water and pretend they are dead. | yes |
| 215 t18-19 S | Once the temperature goes up, the partition bends allowing one ball to fall through. | Once the temperature goes up, the bimetal sheet bends allowing one ball to fall through. | yes |
| 215 b21-15 Q | Soviet Patent no. 1069931. "Meter for counting mould castings". | [The structure of this device is not easy to understand. Is there a figure?] | |
| 216 t1 E | when external layers are cooled, and the internal layers that prevent them from shrinking. | when external layers are cooled, the internal layers prevent them from shrinking. | ok |
| 216 b13 Q | A short stretch of the wire (or a bar secured with the wire) is be made of nitinol | A short stretch of the wire (or a bar holding the wire) is made of nitinol | yes |
| 217 t2 S | corund balls of 40-50 mcm diameter should be | corundum balls of 40-50 ?m diameter should be | yes |
| 217 t3 Q | They disperse the beam without being heated. | They scatter the beam without being heated. | yes |
| 217 t6-7 Q | The upper (driving) cylinder is submerged into a bath with water. | [Isn't it the lower cylinder?] | Lower cylinder |
| 217 b14-12 Q | [Answer to Problem 80.] | [I do not understand in which sense this answer performs high efficiency. Probably, the requests of Problem 80 are not stated clearly enough.] | Efficiency
of any machine can be regarded as maximal delivery of its function under
minimal energy and material expenses.
In case of the vibrator, a high efficiency is reached when vibrations with the required amplitude are excited under minimal power of the electrical motor. But it is difficult to initiate rotation of the flywheel with immovable center of gravity which is positioned remotely from the rotation axis. A powerful electrical motor is needed. It was proposed to make the gravity center movable: when the rotation is initiated, the gravity center is on the rotation axis, and then it is moved to the required position. |
| 218 t12 Q/S | Then, it should be connected to a source of weak current; | Then, it should be connected to one end of a source of weak current and the solution to the other end; | Yes |
| 218 b10-9 S | When the water freezes, the bottle is laid on one side. If thawing occurs | When the water freezes, the bottle is laid on one side. After being frozen, the bottle is put upright. If thawing occurs | Yes |
| 218 b8 S | The width of the horizontal layer | The depth of the horizontal layer | yes (we used to say in this way in Russian: width of a layer) |
| 218 b4 Q/S | Oxygen disappears from the sucker, leaving vacuum inside | Oxygen
disappears from the sucker, reducing the pressure
inside
[How do you treat nitrogen in the air? Do you intend to replace the air in the sucker with oxygen and hydrogen with exact 1:2 proportion of volume? How is it done easily?] |
Because nitrogen is not changed. Under the relation O2 : H2 = 1:2, the whole volumes of O2 and H2 are converted to water, if the ratio is different, only parts of their volumes will be converted. In the first case we have a higher state of vacuum than in the second case. Exact ratio can be provided by the exact measuring of the weight of hydride. This solution might appear to be complex for home appliances, but it is suitable for industrial purposes. Main idea of this example is to show that the vacuum can be obtained without the vacuum pump. |
| 219 t20 E/Q | Electric current is transferred through the thread. Outside a strong electromagnet is turned on. | Electric
current is transferred through the wire. Outside
a strong electromagnet is turned on.
[With this setting, what effect will happen? Does the wire cut the crystal more sharply? Is the wire more durable? Why?] |
If a conductor with electrical current is placed to the permanent magnetic field, it will be subjected to the Lorentz force. This force is oriented towards against deflection of the conductor. The force will become stronger under the higher speed of movement or the higher intensity of the magnetic field. If to select a proper intensity of the magnetic field, the wire will not deflect at all thus providing the high accuracy and quality of cutting. |
| 219 b15-11 Q | analysis of dispersed composition of sprays by precipitation of particles on a filtering surface. Innovative features of the method: to speed up the process, the quantity of sediment is measured by the electric charge transferred by the particles under a potential difference. | [What kind of particles are precipitated? and how? What kind of material is the filtering surface made of? Why is this surface called 'filtering' surface?] | Dispersed
particles are the particles of dust, smoke, mist.
When the air sample is taken for ecological examinations, then a simple device is used: the air catcher. The device is similar to a syringe, in which the air intake with a filter is made instead of a needle. The weight of the filter is measured before and after the air intake. In this invention, it is proposed to measure electrical charges which are brought along with the particles. Now there is no need for exact measurement of the weight. A new feature appears: now it is possible to calculate the number of particles and not only their total weight. The material of the filter's surface might be almost everything, but it must be dielectric. |
| Salamatov's Textbook top page | Errata and Q&A top page | Top of this page | Previous Chapter | Next Chapter |
| Home Page | New Information | Introduction to TRIZ | TRIZ References | TRIZ Links |
| TRIZ News & Activities | TRIZ Software Tools | TRIZ Papers and Tech Reports | TRIZ Forum |
Last updated
on Nov. 22, 2000. Access point: Editor: nakagawa@utc.osaka-gu.ac.jp